-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
[SYCL][SPIR-V Backend] Add SPIR-V backend support inside clang-sycl-linker #3
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
base: master
Are you sure you want to change the base?
Conversation
Signed-off-by: Arvind Sudarsanam <[email protected]>
Signed-off-by: Arvind Sudarsanam <[email protected]>
Signed-off-by: Arvind Sudarsanam <[email protected]>
Signed-off-by: Arvind Sudarsanam <[email protected]>
Signed-off-by: Arvind Sudarsanam <[email protected]>
| // Correct the Triple value if needed | ||
| // TODO: Remove this correction once we start using spirv64/spirv32 triples | ||
| // everywhere. | ||
| Triple TargetTriple(M->getTargetTriple()); | ||
| if (TargetTriple.isSPIR()) { | ||
| TargetTriple.setArch(TargetTriple.getArch() == Triple::spir64 | ||
| ? Triple::spirv64 | ||
| : Triple::spirv32, | ||
| TargetTriple.getSubArch()); | ||
| M->setTargetTriple(TargetTriple); | ||
| // We need to reset Data Layout to conform with the TargetMachine | ||
| M->setDataLayout(""); | ||
| } | ||
| if (TargetTriple.getTriple().empty()) | ||
| TargetTriple.setTriple(DefaultTriple); | ||
| TargetTriple.setArch(TargetTriple.getArch(), Triple::SPIRVSubArch_v16); | ||
| M->setTargetTriple(TargetTriple); | ||
|
|
||
| std::string Msg; | ||
| const Target *T = TargetRegistry::lookupTarget(M->getTargetTriple(), Msg); | ||
| if (!T) | ||
| return createStringError(Msg + ": " + M->getTargetTriple().str()); |
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
@VyacheslavLevytskyy, do we need any of this code? What will happen if SPIR-V backend compile LLVM module with spir (not spirv) target triple?
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
Hi @bader
This is a good catch. I do not think we need this check here. We can work on the premise that the SYCL compilation flow will use spirv32/spirv64 as triples for JIT compilations.
I tried with spir64 triple and I get the following error:
TargetTriple = spir64-unknown-unknown
clang-sycl-linker: error: No available targets are compatible with triple "spir64-unknown-unknown": spir64-unknown-unknown
I will remove the checks and update the tests to create fat objects using SPIRV triples.
Thanks
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
LGTM, except the question about module triple manipulation.
Thanks!
… -arch options to clang-sycl-linker Signed-off-by: Arvind Sudarsanam <[email protected]>
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
just nits
Signed-off-by: Arvind Sudarsanam <[email protected]>
Signed-off-by: Arvind Sudarsanam <[email protected]>
|
Thank you, looks good overall. I have just two comments, more like thoughts aloud.
|
Shouldn't SPIR-V backend use minimal required version? I mean if set 1.6, but all features are present in 1.2, I would expect produced SPIR-V module require 1.2. |
It's hard to imagine a sensible real-world use case, but I can think about an artificial case. E.g., an end-user requires to get the SPV_KHR_float_controls capability in the output to make his hardware-specific code happy and the way to do this in the backend would be to limit the SPIR-V version by 1.3 maximum. Now in this PR the highly hypothetical end-user has no means to control the output in this sense, always getting v1.6 and assumption that this version is supported by the toolchain. Originally, in the SPIR-V backend, we have a way to satisfy this use case by providing So my question was whether such use cases are anticipated enough to secure a way to set a required max SPIR-V version in the PR. |
Signed-off-by: Arvind Sudarsanam <[email protected]>
Signed-off-by: Arvind Sudarsanam <[email protected]>
Hi all, Thanks for the discussion here. As far as SYCL compiler is concerned, I do not see any use facing option to set the SPIR-V version. There is an internal option --spirv-max-version which is hard-coded by the front-end and sent to the spirv-llvm-translator via an option. I am not sure how this can be mapped to the version information inside SPIR-V triple in the case of SPIR-V backend. Thanks |
|
I might be missing some details, but in general llvm-spirv logic is the following: 1.1 if subarch version is set and it's not conflicting with --spirv-max-version option - it picks subarch version, if no conflics with minimum required version; 2.1. if subarch version is not set - check the minimum required version for the module, if not conflicting with --spirv-max-version option - set minimum required version as the module's version; for 1.1 ... 1.3 see KhronosGroup/SPIRV-LLVM-Translator#1516 |
|
I had an offline discussion with Dmitry. The only way the SPIR-V version can be specified is by the user via the target triple SYCL driver team will provide this support. I will make changes accordingly. Thanks |
…triple Signed-off-by: Arvind Sudarsanam <[email protected]>
Signed-off-by: Arvind Sudarsanam <[email protected]>
Do you suggest applying llvm-spirv logic to SPIR-V backend? |
| def arch_EQ : Joined<["--", "-"], "arch=">, | ||
| Flags<[LinkerOnlyOption]>, | ||
| MetaVarName<"<arch>">, | ||
| HelpText<"The device subarchitecture">; |
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
| HelpText<"The device subarchitecture">; | |
| HelpText<"The device architecture">; |
|
|
||
| /// Run LLVM to SPIR-V translation. | ||
| /// Converts 'File' from LLVM bitcode to SPIR-V format using llvm-spirv tool. | ||
| /// Converts 'File' from LLVM bitcode to SPIR-V format using SPIR-V backend. |
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
I think we need to stack this on top of the #4.
There will be a few changes needed to merge them both:
- Linker can pass LLVM Module to the CodeGen instead of write-to-file + read-from-file
- Tests will be updated. E.g. the first check in clang/test/Driver/clang-sycl-linker-test.cpp creates two inputs for linking which define the same symbols. The test will fail if we add [clang-sycl-linker] Replace llvm-link with API calls #4 changes.
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
Hmm. A good point. We might want to hold off this change (to use LLVM Module) as we will be introducing a PR soon to incorporate sycl-post-link based calls
The test won't fail as both the tests do not have any symbols in them.
Thanks
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
I will wait for the llvm-linker changes to be merged upstream before proceeding with this one.
Thanks
No, I'm just describing, how it works now. With introduction of SPIR-V subarch - max-version option seem to be redundant. |
…ctor-bits=128." (llvm#134997) Reverts llvm#134068 Caused a stage 2 build failure: https://lab.llvm.org/buildbot/#/builders/41/builds/6016 ``` FAILED: lib/Support/CMakeFiles/LLVMSupport.dir/Caching.cpp.o /home/tcwg-buildbot/worker/clang-aarch64-sve-vla-2stage/stage1.install/bin/clang++ -DGTEST_HAS_RTTI=0 -D_DEBUG -D_GLIBCXX_ASSERTIONS -D_GNU_SOURCE -D__STDC_CONSTANT_MACROS -D__STDC_FORMAT_MACROS -D__STDC_LIMIT_MACROS -I/home/tcwg-buildbot/worker/clang-aarch64-sve-vla-2stage/stage2/lib/Support -I/home/tcwg-buildbot/worker/clang-aarch64-sve-vla-2stage/llvm/llvm/lib/Support -I/home/tcwg-buildbot/worker/clang-aarch64-sve-vla-2stage/stage2/include -I/home/tcwg-buildbot/worker/clang-aarch64-sve-vla-2stage/llvm/llvm/include -mcpu=neoverse-512tvb -mllvm -scalable-vectorization=preferred -mllvm -treat-scalable-fixed-error-as-warning=false -fPIC -fno-semantic-interposition -fvisibility-inlines-hidden -Werror=date-time -Werror=unguarded-availability-new -Wall -Wextra -Wno-unused-parameter -Wwrite-strings -Wcast-qual -Wmissing-field-initializers -pedantic -Wno-long-long -Wc++98-compat-extra-semi -Wimplicit-fallthrough -Wcovered-switch-default -Wno-noexcept-type -Wnon-virtual-dtor -Wdelete-non-virtual-dtor -Wsuggest-override -Wno-comment -Wstring-conversion -Wmisleading-indentation -Wctad-maybe-unsupported -fdiagnostics-color -ffunction-sections -fdata-sections -Werror=global-constructors -O3 -DNDEBUG -std=c++17 -UNDEBUG -fno-exceptions -funwind-tables -fno-rtti -MD -MT lib/Support/CMakeFiles/LLVMSupport.dir/Caching.cpp.o -MF lib/Support/CMakeFiles/LLVMSupport.dir/Caching.cpp.o.d -o lib/Support/CMakeFiles/LLVMSupport.dir/Caching.cpp.o -c /home/tcwg-buildbot/worker/clang-aarch64-sve-vla-2stage/llvm/llvm/lib/Support/Caching.cpp Opcode has unknown scale! UNREACHABLE executed at ../llvm/llvm/lib/Target/AArch64/AArch64InstrInfo.cpp:4530! PLEASE submit a bug report to https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project/issues/ and include the crash backtrace, preprocessed source, and associated run script. Stack dump: 0. Program arguments: /home/tcwg-buildbot/worker/clang-aarch64-sve-vla-2stage/stage1.install/bin/clang++ -DGTEST_HAS_RTTI=0 -D_DEBUG -D_GLIBCXX_ASSERTIONS -D_GNU_SOURCE -D__STDC_CONSTANT_MACROS -D__STDC_FORMAT_MACROS -D__STDC_LIMIT_MACROS -I/home/tcwg-buildbot/worker/clang-aarch64-sve-vla-2stage/stage2/lib/Support -I/home/tcwg-buildbot/worker/clang-aarch64-sve-vla-2stage/llvm/llvm/lib/Support -I/home/tcwg-buildbot/worker/clang-aarch64-sve-vla-2stage/stage2/include -I/home/tcwg-buildbot/worker/clang-aarch64-sve-vla-2stage/llvm/llvm/include -mcpu=neoverse-512tvb -mllvm -scalable-vectorization=preferred -mllvm -treat-scalable-fixed-error-as-warning=false -fPIC -fno-semantic-interposition -fvisibility-inlines-hidden -Werror=date-time -Werror=unguarded-availability-new -Wall -Wextra -Wno-unused-parameter -Wwrite-strings -Wcast-qual -Wmissing-field-initializers -pedantic -Wno-long-long -Wc++98-compat-extra-semi -Wimplicit-fallthrough -Wcovered-switch-default -Wno-noexcept-type -Wnon-virtual-dtor -Wdelete-non-virtual-dtor -Wsuggest-override -Wno-comment -Wstring-conversion -Wmisleading-indentation -Wctad-maybe-unsupported -fdiagnostics-color -ffunction-sections -fdata-sections -Werror=global-constructors -O3 -DNDEBUG -std=c++17 -UNDEBUG -fno-exceptions -funwind-tables -fno-rtti -MD -MT lib/Support/CMakeFiles/LLVMSupport.dir/Caching.cpp.o -MF lib/Support/CMakeFiles/LLVMSupport.dir/Caching.cpp.o.d -o lib/Support/CMakeFiles/LLVMSupport.dir/Caching.cpp.o -c /home/tcwg-buildbot/worker/clang-aarch64-sve-vla-2stage/llvm/llvm/lib/Support/Caching.cpp 1. <eof> parser at end of file 2. Code generation 3. Running pass 'Function Pass Manager' on module '/home/tcwg-buildbot/worker/clang-aarch64-sve-vla-2stage/llvm/llvm/lib/Support/Caching.cpp'. 4. Running pass 'AArch64 load / store optimization pass' on function '@"_ZNSt17_Function_handlerIFN4llvm8ExpectedISt8functionIFNS1_ISt10unique_ptrINS0_16CachedFileStreamESt14default_deleteIS4_EEEEjRKNS0_5TwineEEEEEjNS0_9StringRefESB_EZNS0_10localCacheESB_SB_SB_S2_IFvjSB_S3_INS0_12MemoryBufferES5_ISH_EEEEE3$_0E9_M_invokeERKSt9_Any_dataOjOSF_SB_"' #0 0x0000b6eae9b67bf0 llvm::sys::PrintStackTrace(llvm::raw_ostream&, int) (/home/tcwg-buildbot/worker/clang-aarch64-sve-vla-2stage/stage1.install/bin/clang+++0x81c7bf0) #1 0x0000b6eae9b65aec llvm::sys::RunSignalHandlers() (/home/tcwg-buildbot/worker/clang-aarch64-sve-vla-2stage/stage1.install/bin/clang+++0x81c5aec) #2 0x0000b6eae9acd5f4 CrashRecoverySignalHandler(int) CrashRecoveryContext.cpp:0:0 #3 0x0000f16c1aff28f8 (linux-vdso.so.1+0x8f8) #4 0x0000f16c1aacf1f0 __pthread_kill_implementation ./nptl/pthread_kill.c:44:76 #5 0x0000f16c1aa8a67c gsignal ./signal/../sysdeps/posix/raise.c:27:6 #6 0x0000f16c1aa77130 abort ./stdlib/abort.c:81:7 llvm#7 0x0000b6eae9ad6628 (/home/tcwg-buildbot/worker/clang-aarch64-sve-vla-2stage/stage1.install/bin/clang+++0x8136628) llvm#8 0x0000b6eae72e95a8 (/home/tcwg-buildbot/worker/clang-aarch64-sve-vla-2stage/stage1.install/bin/clang+++0x59495a8) llvm#9 0x0000b6eae74ca9a8 (anonymous namespace)::AArch64LoadStoreOpt::findMatchingInsn(llvm::MachineInstrBundleIterator<llvm::MachineInstr, false>, (anonymous namespace)::LdStPairFlags&, unsigned int, bool) AArch64LoadStoreOptimizer.cpp:0:0 llvm#10 0x0000b6eae74c85a8 (anonymous namespace)::AArch64LoadStoreOpt::tryToPairLdStInst(llvm::MachineInstrBundleIterator<llvm::MachineInstr, false>&) AArch64LoadStoreOptimizer.cpp:0:0 llvm#11 0x0000b6eae74c624c (anonymous namespace)::AArch64LoadStoreOpt::optimizeBlock(llvm::MachineBasicBlock&, bool) AArch64LoadStoreOptimizer.cpp:0:0 llvm#12 0x0000b6eae74c429c (anonymous namespace)::AArch64LoadStoreOpt::runOnMachineFunction(llvm::MachineFunction&) AArch64LoadStoreOptimizer.cpp:0:0 ```
…vailable (llvm#135343) When a frame is inlined, LLDB will display its name in backtraces as follows: ``` * thread #1, queue = 'com.apple.main-thread', stop reason = breakpoint 1.3 * frame #0: 0x0000000100000398 a.out`func() [inlined] baz(x=10) at inline.cpp:1:42 frame #1: 0x0000000100000398 a.out`func() [inlined] bar() at inline.cpp:2:37 frame #2: 0x0000000100000398 a.out`func() at inline.cpp:4:15 frame #3: 0x00000001000003c0 a.out`main at inline.cpp:7:5 frame #4: 0x000000026eb29ab8 dyld`start + 6812 ``` The longer the names get the more confusing this gets because the first function name that appears is the parent frame. My assumption (which may need some more surveying) is that for the majority of cases we only care about the actual frame name (not the parent). So this patch removes all the special logic that prints the parent frame. Another quirk of the current format is that the inlined frame name does not abide by the `${function.name-XXX}` format variables. We always just print the raw demangled name. With this patch, we would format the inlined frame name according to the `frame-format` setting (see the test-cases). If we really want to have the `parentFrame [inlined] inlinedFrame` format, we could expose it through a new `frame-format` variable (e..g., `${function.inlined-at-name}` and let the user decide where to place things.
…reporting (llvm#131756) ### Description This PR resolves a deadlock between AddressSanitizer (ASan) and LeakSanitizer (LSan) that occurs when both sanitizers attempt to acquire locks in conflicting orders across threads. The fix ensures safe lock acquisition ordering by preloading module information before error reporting. --- ### Issue Details **Reproducer** ```cpp // Thread 1: ASan error path int arr[1] = {0}; std::thread t([&]() { arr[1] = 1; // Triggers ASan OOB error }); // Thread 2: LSan check path __lsan_do_leak_check(); ``` **Lock Order Conflict**: - Thread 1 (ASan error reporting): 1. Acquires ASan thread registry lock (B) 1. Attempts to acquire libdl lock (A) via `dl_iterate_phdr` - Thread 2 (LSan leak check): 1. Acquires libdl lock (A) via `dl_iterate_phdr` 1. Attempts to acquire ASan thread registry lock (B) This creates a circular wait condition (A -> B -> A) meeting all four Coffman deadlock criteria. --- ### Fix Strategy The root cause lies in ASan's error reporting path needing `dl_iterate_phdr` (requiring lock A) while already holding its thread registry lock (B). The solution: 1. **Preload Modules Early**: Force module list initialization _before_ acquiring ASan's thread lock 2. **Avoid Nested Locking**: Ensure symbolization (via dl_iterate_phdr) completes before error reporting locks Key code change: ```cpp // Before acquiring ASan's thread registry lock: Symbolizer::GetOrInit()->GetRefreshedListOfModules(); ``` This guarantees module information is cached before lock acquisition, eliminating the need for `dl_iterate_phdr` calls during error reporting. --- ### Testing Added **asan_lsan_deadlock.cpp** test case: - Reproduces deadlock reliably without fix **under idle system conditions** - Uses watchdog thread to detect hangs - Verifies ASan error reports correctly without deadlock **Note**: Due to the inherent non-determinism of thread scheduling and lock acquisition timing, this test may not reliably reproduce the deadlock on busy systems (e.g., during parallel `ninja check-asan` runs). --- ### Impact - Fixes rare but severe deadlocks in mixed ASan+LSan environments - Maintains thread safety guarantees for both sanitizers - No user-visible behavior changes except deadlock elimination --- ### Relevant Buggy Code - Code in ASan's asan_report.cpp ```cpp explicit ScopedInErrorReport(bool fatal = false) : halt_on_error_(fatal || flags()->halt_on_error) { // Acquire lock B asanThreadRegistry().Lock(); } ~ScopedInErrorReport() { ... // Try to acquire lock A under holding lock B via the following path // #4 0x000071a353d83e93 in __GI___dl_iterate_phdr ( // callback=0x5d1a07a39580 <__sanitizer::dl_iterate_phdr_cb(dl_phdr_info*, unsigned long, void*)>, // data=0x6da3510fd3f0) at ./elf/dl-iteratephdr.c:39 // #5 0x00005d1a07a39574 in __sanitizer::ListOfModules::init (this=0x71a353ebc080) // at llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/sanitizer_common/sanitizer_linux_libcdep.cpp:784 // #6 0x00005d1a07a429e3 in __sanitizer::Symbolizer::RefreshModules (this=0x71a353ebc058) // at llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/sanitizer_common/sanitizer_symbolizer_libcdep.cpp:188 // llvm#7 __sanitizer::Symbolizer::FindModuleForAddress (this=this@entry=0x71a353ebc058, // address=address@entry=102366378805727) // at llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/sanitizer_common/sanitizer_symbolizer_libcdep.cpp:214 // llvm#8 0x00005d1a07a4291b in __sanitizer::Symbolizer::SymbolizePC (this=0x71a353ebc058, addr=102366378805727) // at llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/sanitizer_common/sanitizer_symbolizer_libcdep.cpp:88 // llvm#9 0x00005d1a07a40df7 in __sanitizer::(anonymous namespace)::StackTraceTextPrinter::ProcessAddressFrames ( // this=this@entry=0x6da3510fd520, pc=102366378805727) // at llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/sanitizer_common/sanitizer_stacktrace_libcdep.cpp:37 // llvm#10 0x00005d1a07a40d27 in __sanitizer::StackTrace::PrintTo (this=this@entry=0x6da3510fd5e8, // output=output@entry=0x6da3510fd588) // at llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/sanitizer_common/sanitizer_stacktrace_libcdep.cpp:110 // llvm#11 0x00005d1a07a410a1 in __sanitizer::StackTrace::Print (this=0x6da3510fd5e8) // at llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/sanitizer_common/sanitizer_stacktrace_libcdep.cpp:133 // llvm#12 0x00005d1a0798758d in __asan::ErrorGeneric::Print ( // this=0x5d1a07aa4e08 <__asan::ScopedInErrorReport::current_error_+8>) // at llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/asan/asan_errors.cpp:617 current_error_.Print(); ... } ``` - Code in LSan's lsan_common_linux.cpp ```cpp void LockStuffAndStopTheWorld(StopTheWorldCallback callback, CheckForLeaksParam *argument) { // Acquire lock A dl_iterate_phdr(LockStuffAndStopTheWorldCallback, ¶m); } static int LockStuffAndStopTheWorldCallback(struct dl_phdr_info *info, size_t size, void *data) { // Try to acquire lock B under holding lock A via the following path // #3 0x000055555562b34a in __sanitizer::ThreadRegistry::Lock (this=<optimized out>) // at llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/asan/../sanitizer_common/sanitizer_thread_registry.h:99 // #4 __lsan::LockThreads () at llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/asan/asan_thread.cpp:484 // #5 0x0000555555652629 in __lsan::ScopedStopTheWorldLock::ScopedStopTheWorldLock (this=<optimized out>) // at llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/lsan/lsan_common.h:164 // #6 __lsan::LockStuffAndStopTheWorldCallback (info=<optimized out>, size=<optimized out>, data=0x0, // data@entry=0x7fffffffd158) at llvm-project/compiler-rt/lib/lsan/lsan_common_linux.cpp:120 ScopedStopTheWorldLock lock; DoStopTheWorldParam *param = reinterpret_cast<DoStopTheWorldParam *>(data); StopTheWorld(param->callback, param->argument); return 1; } ```
Fixes llvm#123300 What is seen ``` clang-repl> int x = 42; clang-repl> auto capture = [&]() { return x * 2; }; In file included from <<< inputs >>>:1: input_line_4:1:17: error: non-local lambda expression cannot have a capture-default 1 | auto capture = [&]() { return x * 2; }; | ^ zsh: segmentation fault clang-repl --Xcc="-v" (lldb) bt * thread #1, queue = 'com.apple.main-thread', stop reason = EXC_BAD_ACCESS (code=1, address=0x8) * frame #0: 0x0000000107b4f8b8 libclang-cpp.19.1.dylib`clang::IncrementalParser::CleanUpPTU(clang::PartialTranslationUnit&) + 988 frame #1: 0x0000000107b4f1b4 libclang-cpp.19.1.dylib`clang::IncrementalParser::ParseOrWrapTopLevelDecl() + 416 frame #2: 0x0000000107b4fb94 libclang-cpp.19.1.dylib`clang::IncrementalParser::Parse(llvm::StringRef) + 612 frame #3: 0x0000000107b52fec libclang-cpp.19.1.dylib`clang::Interpreter::ParseAndExecute(llvm::StringRef, clang::Value*) + 180 frame #4: 0x0000000100003498 clang-repl`main + 3560 frame #5: 0x000000018d39a0e0 dyld`start + 2360 ``` Though the error is justified, we shouldn't be interested in exiting through a segfault in such cases. The issue is that empty named decls weren't being taken care of resulting into this assert https://github.com/llvm/llvm-project/blob/c1a229252617ed58f943bf3f4698bd8204ee0f04/clang/include/clang/AST/DeclarationName.h#L503 Can also be seen when the example is attempted through xeus-cpp-lite. 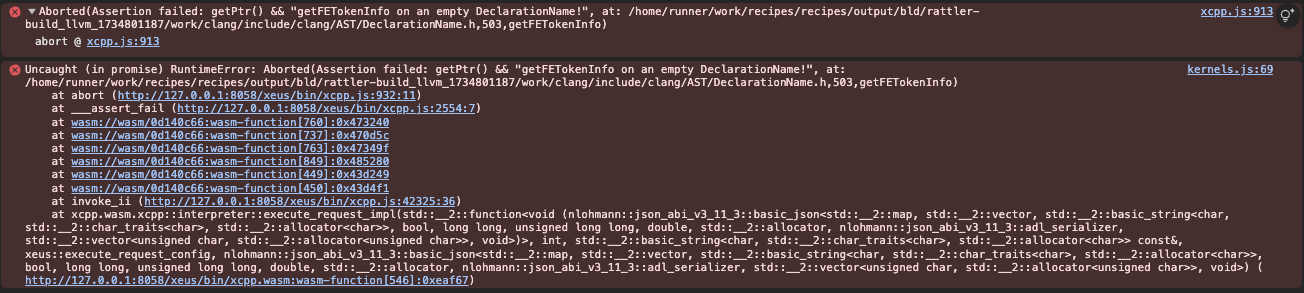
…142952) This was removed in llvm#135343 in favour of making it a format variable, which we do here. This follows the precedent of the `[opt]` and `[artificial]` markers. Before: ``` thread #1, queue = 'com.apple.main-thread', stop reason = breakpoint 1.2 * frame #0: 0x000000010000037c a.out`inlined1() at inline.cpp:4:3 frame #1: 0x000000010000037c a.out`regular() at inline.cpp:6:17 frame #2: 0x00000001000003b8 a.out`inlined2() at inline.cpp:7:43 frame #3: 0x00000001000003b4 a.out`main at inline.cpp:10:3 frame #4: 0x0000000186345be4 dyld`start + 7040 ``` After (note the `[inlined]` markers): ``` thread #1, queue = 'com.apple.main-thread', stop reason = breakpoint 1.2 * frame #0: 0x000000010000037c a.out`inlined1() at inline.cpp:4:3 [inlined] frame #1: 0x000000010000037c a.out`regular() at inline.cpp:6:17 frame #2: 0x00000001000003b8 a.out`inlined2() at inline.cpp:7:43 [inlined] frame #3: 0x00000001000003b4 a.out`main at inline.cpp:10:3 frame #4: 0x0000000186345be4 dyld`start + 7040 ``` rdar://152642178
This PR does the following:
Currently, all SPIR-V extensions are enabled for SYCL compilation flow. This will be updated in subsequent commits, if needed.
Thanks