Sprout is a lightweight F# test DSL with a clean, composable structure built on computation expressions. This allows your test suites to grow almost organically - i.e. sprout.
🔥 Latest news
- Refactoring for improved extensibility.
- Custom runner support has been added.
- Test ordering is now customizable.
- See Extending Sprout for more details.
- Minimalist & expressive BDD-style syntax
- Nestable
describeblocks for organizing tests to any depth or complexity - Computation expressions for
it,beforeEach,afterEach - Asynchronous blocks supported
- Pending tests support
- Logging for improved traceability
- Built-in assertions:
shouldEqual,shouldNotEqual,shouldBeTrue,shouldBeFalse- These go a long way towards making your tests readable and expressive due to the
descriptive text that goes along with each
describeblock andittest case. Note that you may use any exception-based constraints library if desired (FsUnit.Light works beautifully).
- These go a long way towards making your tests readable and expressive due to the
descriptive text that goes along with each
- Support for parameterized tests using normal F# loops within
describeblocks - Pluggable reporters (console, silent, TAP, JSON)
- Built for F# — simple and idiomatic
- No need for
<|or functions wrapped in parentheses! - No need for complex combinations of attributes - it's all just F# code!
- No need for
Sprout provides a clean API for structuring tests. There are a minimum of
abstractions. describe blocks may be nested to any suitable depth. It is
only a matter of composing the building blocks. Just like you would expect
coming from a functional programming background.
dotnet add package dlidstrom.Sprout#load "Sprout.fs"
open Sprout
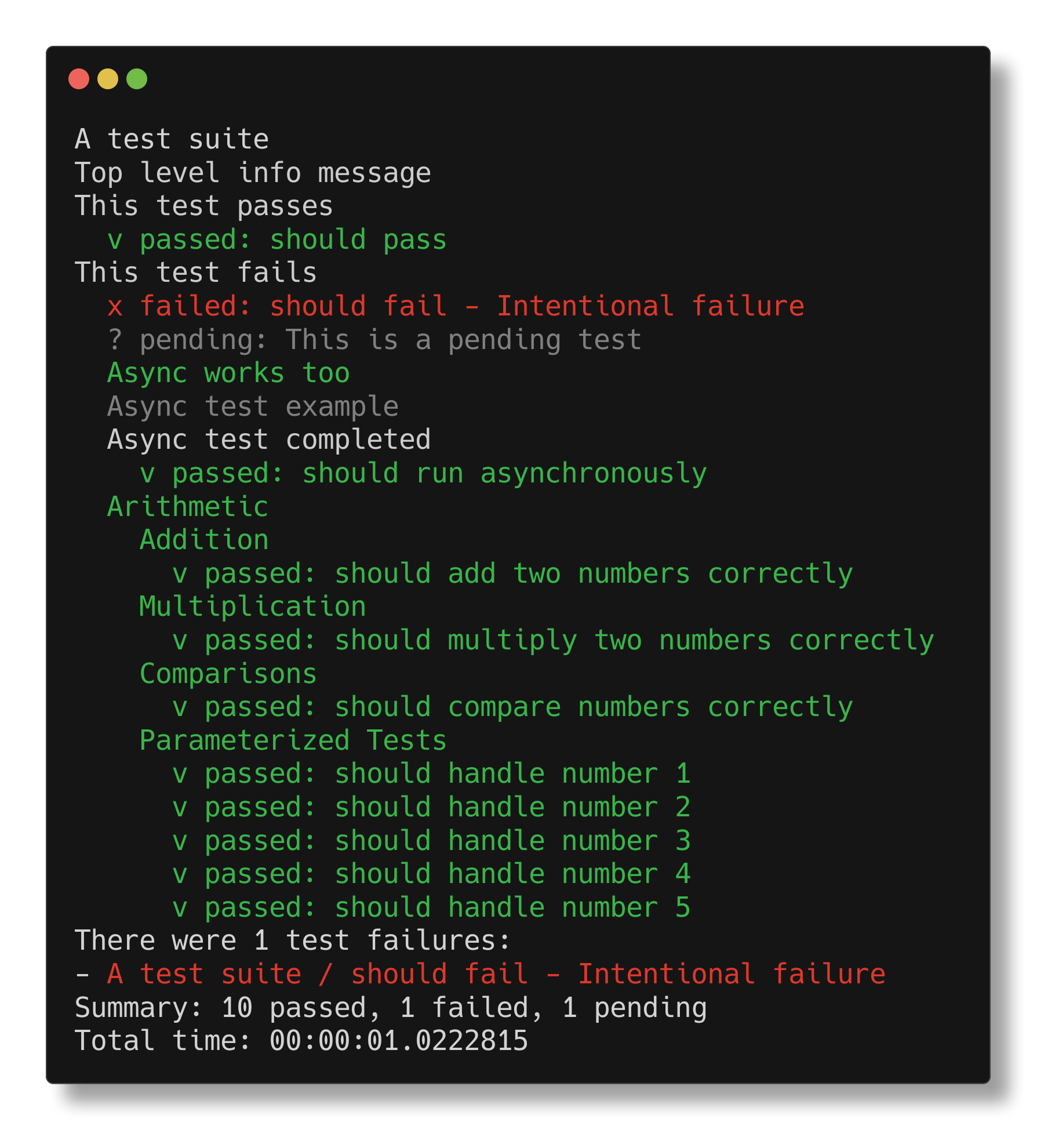
let suite = describe "A test suite" {
Info "Top level info message"
// variables may be used to store state across tests
let mutable b = false
beforeEach { b <- true }
it "should pass" {
info "This test passes"
// simple assertions included out-of-the-box
b |> shouldBeTrue
}
it "should fail" {
info "This test fails"
failwith "Intentional failure"
}
// use pending to mark tests that are not yet implemented
pending "This is a pending test"
describe "Async works too" {
Debug "Async test example"
// asynchronous flows are supported
it "should run asynchronously" {
do! Async.Sleep 1000
info "Async test completed"
}
}
// use nested suites to organize tests
describe "Arithmetic" {
describe "Addition" {
it "should add two numbers correctly" {
let result = 2 + 2
result |> shouldEqual 4
}
}
describe "Multiplication" {
it "should multiply two numbers correctly" {
let result = 3 * 3
result |> shouldEqual 9
}
}
describe "Comparisons" {
debug "Testing comparisons"
it "should compare numbers correctly" {
5 > 3 |> shouldBeTrue
}
}
// parameterized tests are supported using regular F# loops
// type-safe as expected without any special syntax
describe "Parameterized Tests" {
info "Simply embed test cases and loop over them"
let numbers = [1; 2; 3; 4; 5]
for n in numbers do
it $"should handle number {n}" {
n > 0 |> shouldBeTrue
}
}
}
}
runTestSuiteCustom
// id is used to order the tests (it blocks)
// you can specify a custom ordering function if needed
(DefaultRunner(Reporters.ConsoleReporter("v", "x", "?", " "), id))
suite
|> Async.RunSynchronouslyOutput:
| Name | Usage | Supported Expressions |
|---|---|---|
describe |
Declarative | it, beforeEach, afterEach, it, Info, Debug |
it |
Imperative | Any F# expressions, but typically exception-based assertions |
beforeEach, afterEach |
Imperative | Hook functions that run before and after test cases, respectively |
describe- used to define a test suite, or a group of tests. Use the text to create descriptive sentences of expected behaviour.it- used to define test assertions, along with a descriptive text to define the expected behaviourbeforeEach/afterEach- hook functions that run before and after test cases, respectivelypending- used to denote a pending test caseinfo/debug- tracing functions that may be used inside hook functions anditblocksInfo/Debug- constructor functions that provide tracing insidedescribeblocks
Tracing works slightly different in
describeblocks due to limitations of me (most likely) and/or F# computation expressions.
You can plug in your own reporter:
type MyCustomReporter() =
inherit TestReporter()
with
override _.Begin(totalCount) = ...
override _.BeginSuite(name, path) = ...
override _.ReportResult(result, path) = ...
override _.EndSuite(name, path) = ...
override _.Info(message, path) = ...
override _.Debug(message, path) = ...
override _.End(testResults) = ...Use it like this:
let reporter = MyCustomReporter()
let failedCount =
runTestSuiteCustom
// id is used to order the tests (it blocks)
// you can specify a custom ordering function if needed
// advanced use cases might run earlier failed
// tests first
(DefaultRunner(reporter, id))
suite
|> Async.RunSynchronouslyAvailable reporters (available in the Sprout.Reporters namespace):
| Reporter | Description |
|---|---|
ConsoleReporter |
Outputs test results to the console |
TapReporter |
Outputs test results in TAP format |
It is also possible to modify the default or create your own runner. A simple example is to modify the default runner to run tests in parallel, or run a subset of tests:
let parallelRunner = {
new DefaultRunner(Reporters.TapReporter(), id) with
override _.SequenceAsync args = Async.Parallel args }
runTestSuiteCustom
parallelRunner
suite
|> Async.RunSynchronouslyThis is the runner abstract class:
[<AbstractClass>]
type Runner() =
abstract member Run: Describe -> Async<TestResult[]>
abstract member CollectDescribes: Describe -> CollectedDescribe
abstract member RunTestCase: Path -> It -> HookFunctions -> Async<TestResult>
abstract member RunCollectedDescribe: CollectedDescribe -> Async<TestResult[]>
abstract member SequenceAsync: Async<'T> list -> Async<'T array>Sprout is tested using Bash Automated Testing System. Tests are run using the following command:
$ bats .
./test.bats
✓ Tests.fsx
1 test, 0 failures| NuGet | dlidstrom.Sprout |
| Target | .NET Standard 2.0. |
| License | MIT |
| Author | Daniel Lidström |