Docker is a set of platform as a service (PaaS) products that use OS-level virtualization to deliver software in packages called containers. The service has both free and premium tiers. The software that hosts the containers is called Docker Engine. It was first released in 2013 and is developed by Docker, Inc.
Docker is a tool that is used to automate the deployment of applications in lightweight containers so that applications can work efficiently in different environments in isolation.
Ansible is a suite of software tools that enables infrastructure as code. It is open-source and the suite includes software provisioning, configuration management, and application deployment functionality.
Ansible is an open source IT automation engine that automates provisioning, configuration management, application deployment, orchestration, and many other IT processes. It is free to use, and the project benefits from the experience and intelligence of its thousands of contributors.
We have 3 machine, one for ansible management and 2 for hosts to install docker on them :
At first we must install ansible on the DesktopTest (ansible management) :
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:ansible/ansible
sudo apt update
sudo apt install ansible
ansible --version
Note : python must be installed at any linux and consider that we have one linux for source (ansible management node) where the ansible is installed on it and one or many linux for destination that must be install docker by ansible.
Important : management node must can ssh to any destination node passwordlesslly.
for this reason, we generate a ssh key on management node and copy it to any destination nodes.
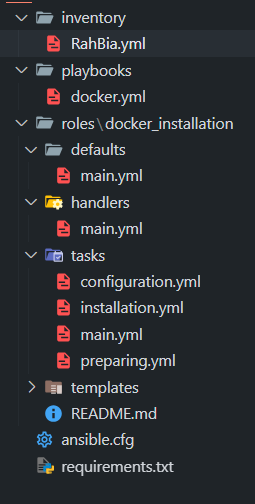
then check the ansible project and files at management node :
The requirements.txt file is used in Python projects to list all the dependencies (external libraries or packages) that are required to run your application or project. This file allows users to easily install the necessary dependencies using pip, the Python package installer.
cd ansible
pip install -r requirements.txt
The ansible.cfg file defines key configuration settings for running Ansible playbooks and managing target servers. This file allows customization of various options, including connection details, logging, and roles directory paths, making it easier to manage Ansible behavior across different environments.
Playbooks are used to execute multiple roles and tasks across targeted servers.
docker.yml This is a Docker playbook that allows us to invoke the Docker role
Each role in this project is modular, focused on a specific area of system security, and designed to be reusable.
docker_installation With this role, you can install and configure Docker.
Edit the inventory file based on destination node(s) :
all:
vars:
ansible_user: root
ansible_port: 22 #8090
hosts:
server01:
ansible_host: 192.168.56.157
server02:
ansible_host: 192.168.56.158
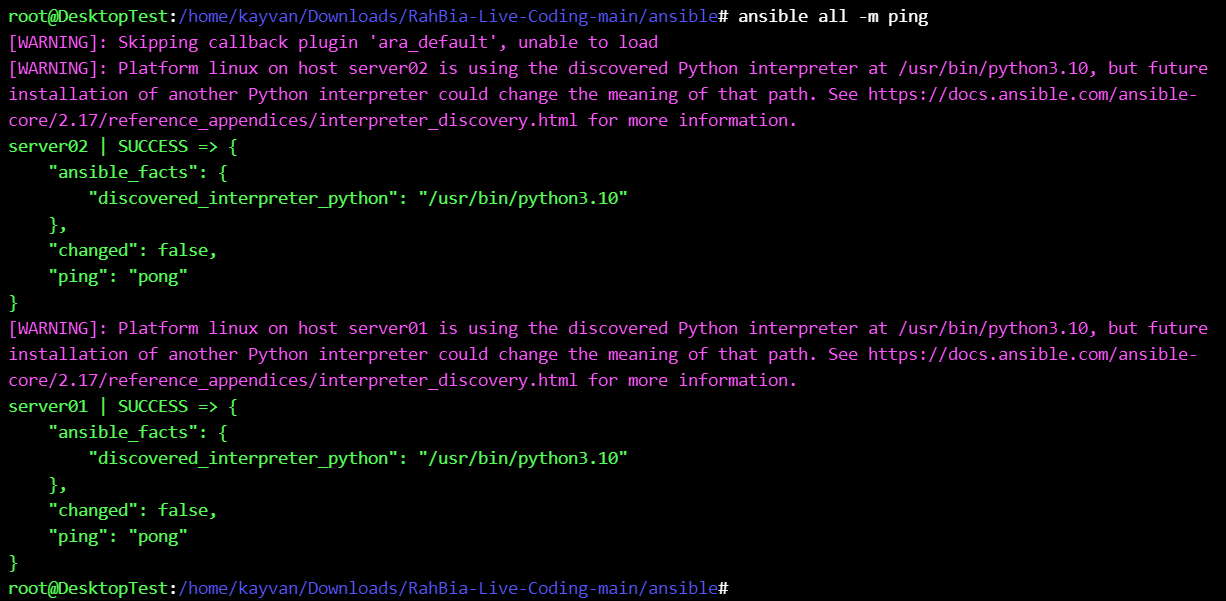
then ping all destination host(s) to be ok before running the ansible playbooks :
ansible all -m ping
check 2 machines that does not have docker installed on them :
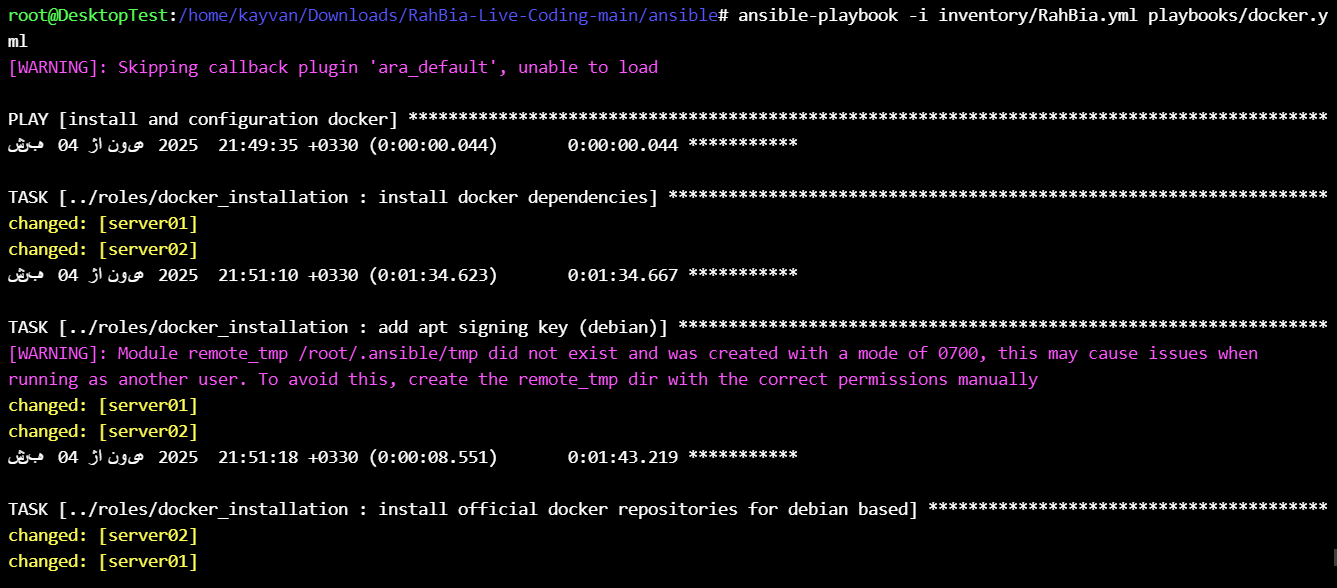
then run the playbook :
ansible-playbook -i inventory/RahBia.yml playbooks/docker.yml
or
ansible-playbook playbooks/docker.yml
htop on one of 2 machine :
if any error happens, check and correct it and run the playbook again.
Note : ansible process is idempotent, an idempotent operation is one that has no additional effect if it is called more than once with the same input parameters.
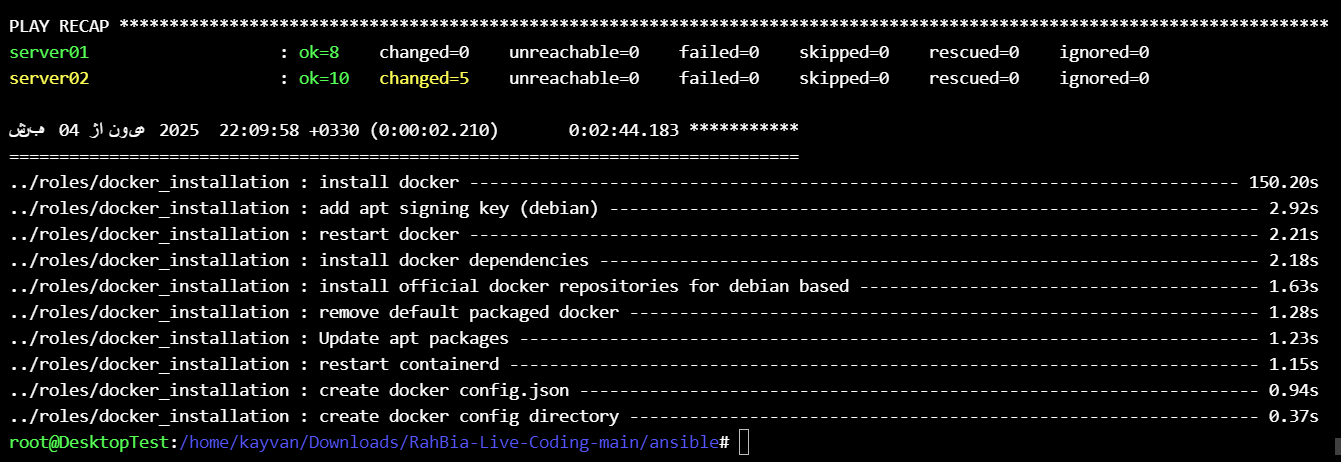
at final we have the result like below :
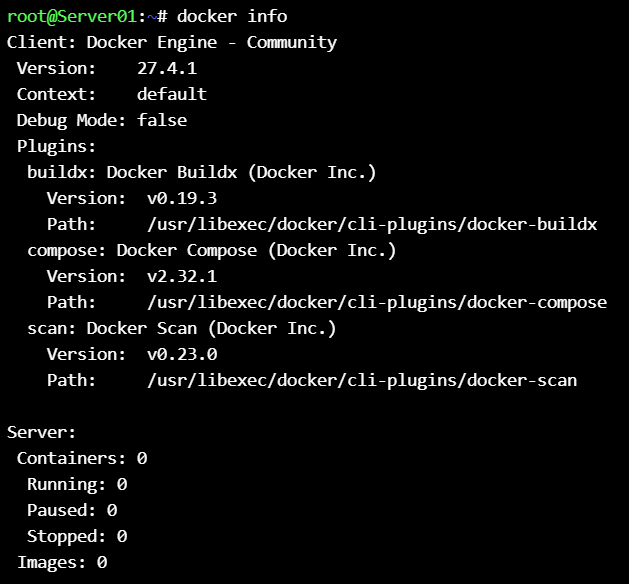
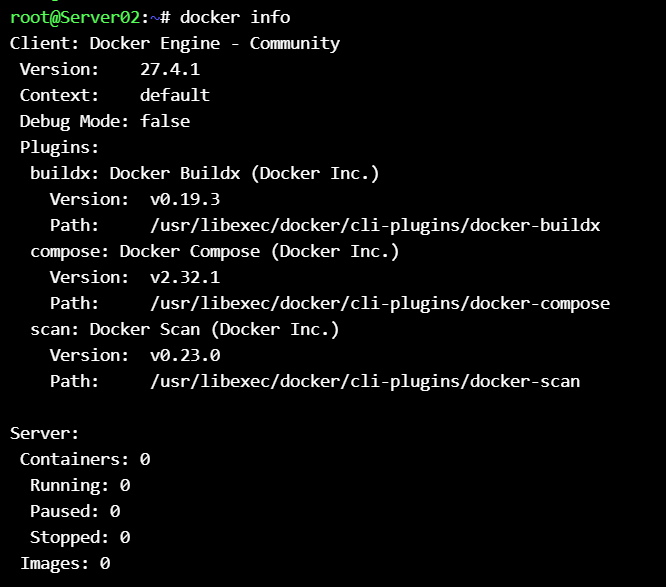
and now check 2 machines that have docker.
Congratulation. 🍹